Palliative Therapy
(26) The Cost of Catheter Dislodgement
Saturday, September 23, 2023
6:00 PM - 7:30 PM East Coast USA Time
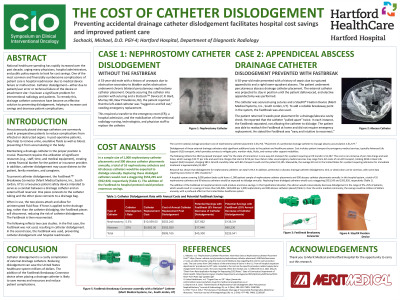
Purpose: Long term care of patient's with complicated disease processes often incurs significant financial burden. This burden if often complicated with misuse or failure of medical devices. One of the most common devices used in parallel with surgical resections/drainages are drainage catheters. These catheters often fail secondary due to dislodgment, kinks, or obstructions.
Material and Methods: Placement of a peritoneal drainage catheter to manage abscess accumulation is $1,577.
Dislodgement of these external drainage catheters adds significant additional costs to the patient and healthcare system. Cost includes patient transport by emergency medical services, typically Advanced Life Support (ALS); one-way ALS transport for a patient requiring an ER transfer is $1,287. This cost is non-inclusive of per mile charge and wait times, which average $19.77 per mile and wait time charges that start at $215 per hour. ALS-ER roundtrip rides with BLS transport could cost the patient $2,105. Meanwhile, the average ER cost in the United States for a patient requiring admission for immediate treatment is approximately $2,200.
Research has shown that dislodgement, kink, or obstruction can be common in peritoneal catheters, with some data reporting occurrence in 20% of patients.
Results: In this hospital system, a total of 55 nephrostomy catheters and 60 abscess catheters would be expected to dislodge annually. Replacing these dislodged catheters would cost a staggering $553,245 and $352,920, respectively.
The addition of the FastBreak to hospital protocol could produce enormous savings.
In this hypothetical situation, this add-on would conservatively decrease dislodgement in the range of 5%–25% of patients, which would result in a savings of more than $45,000– $226,000 per 1,000 nephrostomy and 300 abscess catheters placed.
Over the entire medical community, the savings could be millions of dollars annually, with
a profound effect on the United States healthcare system.
Conclusions: Catheter dislodgement is a costly complication of external drainage catheters. Reducing dislodgement can save the United States healthcare system millions of dollars. The addition of the FastBreak Breakaway Connector device when placing a drainage catheter is likely to save money and resources and reduce patient complications.
Material and Methods: Placement of a peritoneal drainage catheter to manage abscess accumulation is $1,577.
Dislodgement of these external drainage catheters adds significant additional costs to the patient and healthcare system. Cost includes patient transport by emergency medical services, typically Advanced Life Support (ALS); one-way ALS transport for a patient requiring an ER transfer is $1,287. This cost is non-inclusive of per mile charge and wait times, which average $19.77 per mile and wait time charges that start at $215 per hour. ALS-ER roundtrip rides with BLS transport could cost the patient $2,105. Meanwhile, the average ER cost in the United States for a patient requiring admission for immediate treatment is approximately $2,200.
Research has shown that dislodgement, kink, or obstruction can be common in peritoneal catheters, with some data reporting occurrence in 20% of patients.
Results: In this hospital system, a total of 55 nephrostomy catheters and 60 abscess catheters would be expected to dislodge annually. Replacing these dislodged catheters would cost a staggering $553,245 and $352,920, respectively.
The addition of the FastBreak to hospital protocol could produce enormous savings.
In this hypothetical situation, this add-on would conservatively decrease dislodgement in the range of 5%–25% of patients, which would result in a savings of more than $45,000– $226,000 per 1,000 nephrostomy and 300 abscess catheters placed.
Over the entire medical community, the savings could be millions of dollars annually, with
a profound effect on the United States healthcare system.
Conclusions: Catheter dislodgement is a costly complication of external drainage catheters. Reducing dislodgement can save the United States healthcare system millions of dollars. The addition of the FastBreak Breakaway Connector device when placing a drainage catheter is likely to save money and resources and reduce patient complications.
